singularity
- Prototypes
- How are objects linked? Prototypes
- The
prototypeproperty - Getting prototype of any object
Object.prototype- parent of all objectsFunctionfunction- Problems with
__proto__ Object.createmethodNullprototype object- ES2015 classes
Prototypes
-
Inheritance reduces code duplication and promotes code sharing between different objects.
-
the prototype chain - Think of the scope chain, where each scope is linked to another scope until we reach the global scope.
-
The prototype chain is similar: one object is linked to another object.
-
This other object, in turn, is linked to another object, forming a chain between objects.
-
prototypal inheritance When we create an object literal in JavaScript, it is, by default, linked to the built-in
Object.prototypeobject
How are objects linked? Prototypes
-
Objects in JavaScript have a hidden internal slot named
[[Prototype]] -
linked to another object by saving a reference to the other object in the
[[Prototype]]internal slot of the newly created object -
obj.[[Prototype]]gives us the prototype of the obj object -
But as
[[Prototype]]is an internal slot not accessible by JavaScript
The prototype property
Getting prototype of any object
.getPrototypeOf()
Object.prototype - parent of all objects
- At the top of the prototypal inheritance hierarchy is the
Object.prototypeobject. It is the root object or parent of all objects
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) === Object.prototype);
//true
console.log(obj.toString());
// [object Object]
-
As discussed in the previous lesson, functions have a prototype property that points to an object that serves as the prototype of all instances of that function when that function is invoked as a “constructor”.
-
So, the
Object.prototypeobject serves as the “prototype” of all objects created via newObject()or through object literal notation.
Function function
-
there’s a function named Function⁸⁸.
-
Functions in JavaScript are objects and are instances of this “Function” constructor function.
-
Function.prototypeobject provides properties that are accessible by all functions; for example, methods likebind,call,apply, etc. -
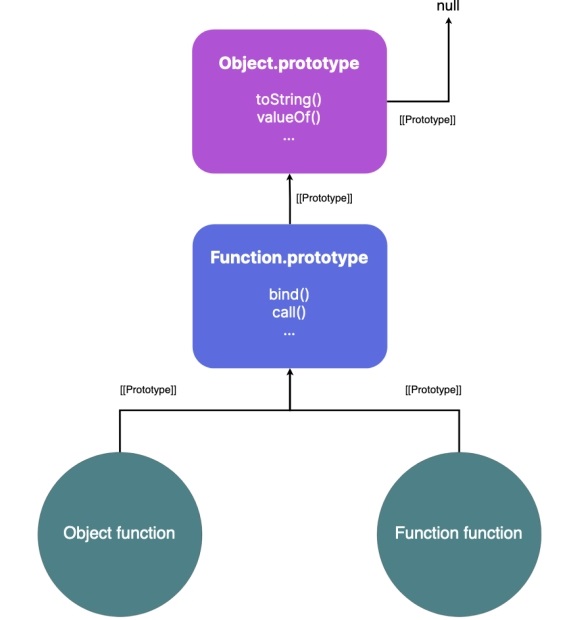
-
The
__proto__property is defined on theObject.prototypeobject. It is a getter and a setter that returns or sets the prototype of an object -
it returns or sets the value of the internal
[[Prototype]]property of an object. -
its use is discouraged property has been deprecated, and better alternatives have been provided (
setPrototypeOf)
Problems with __proto__
-
deprecated
-
not available for all objects
-
not available for custom objects
Object.create method
-
used to create a new object with another object, passed as the first argument, as the prototype of the newly created object.
-
lets us explicitly set the prototype of an object
Null prototype object
-
All objects ultimately inherit from the Object.prototype object because it sits at the top of the prototype chain and is the parent of all objects.
-
However, we can create objects that do not inherit properties from any object.
-
We just have to set null as the value of the internal [[Prototype]] property using the methods discussed above.
const obj = Object.create(null);
console.log(obj.toString());
// Error: toString not defined
- The null prototype objects may seem useless, but they are useful in some cases.
- For example, such objects are safe from attacks such as the prototype pollution attack, where a malicious code might add some properties to the prototype chain of an object that could change the normal flow of code execution.
Object.prototype.isAdmin = true;
ES2015 classes
-
Extending a class creates a parent-child relationship where the child class extends the parent class. It promotes code reusability.
-
Until 2015, JavaScript didn’t have classes. Constructor functions were used instead. To inherit from a constructor function
-
JavaScript developers explicitly created a link between the prototype properties of two different constructor functions by using the
Object.createmethod -
it is error-prone because there are multiple steps to set a prototype link correctly between the two constructors.
-
As of 2015, JavaScript has classes. They provide a declarative way of writing code that is less error-prone.
-
Classes come with the
extendskeyword that helps create a parent-child relationship between classes